Does waxing reduce hair growth, or is it just another beauty myth?
If you’ve been waxing for years, you might notice your hair feels thinner or grows back more slowly.
Many believe waxing slows growth, but the reality is more complex than most assume. Waxing influences how your hair grows, though not always in the way you might think
Some experience slower regrowth after several sessions, while others see only minor changes.
In this blog, I’ll show you exactly how waxing impacts hair growth, what science says about it, and what you can realistically expect from regular waxing sessions.
How Hair Growth Works: The Hair Growth Cycle
Hair growth isn’t simultaneous across your body. Each follicle operates on its own timeline through three distinct phases. This cycle determines when hair appears and how long it stays.
Why does this matter for waxing? Because removing hair at different cycle points produces varying results. Some follicles bounce back quickly, while others take months to regenerate.
| Growth Phase | Duration | What Happens |
|---|---|---|
| Anagen | 2-7 years | Active growth from the root |
| Catagen | 2-3 weeks | Growth stops, follicle shrinks |
| Telogen | 3 months | Hair rests, then falls out |
When hair is pulled from its root, the follicle pauses before regrowing, creating a longer gap between new strands. Hair pulled during telogen was already preparing to shed anyway.
Body location also influences cycle length. Leg hair stays in the growth phase for just a few months. Scalp hair can keep growing for years before entering the resting phase.
What Happens to Hair Follicles During Waxing?
Waxing removes hair from the root, unlike shaving, which only cuts at the surface. Warm wax grips the shaft and pulls the entire strand out when removed quickly.
This leaves the follicle empty and temporarily inactive. It needs time to regenerate new hair, which explains the longer smooth period you experience.
Does waxing damage follicles?
Yes, repeated sessions can weaken them over time. The pulling trauma makes it harder for thick hair to return. Some follicles stop producing hair after years of regular waxing.
Results vary by person. Fine hair weakens faster than coarse hair. You’ll typically notice softer regrowth, lighter color, and potentially reduced density. However, these changes aren’t guaranteed for everyone.
Does Waxing Actually Slow or Reduce Hair Growth?

Yes, waxing can slow hair growth. Since you’re removing hair from the root, regrowth takes much longer than shaving.
Over time, regular waxing sessions may reduce overall hair density. The repeated stress on follicles causes them to weaken and produce finer hair.
What you can expect from regular waxing:
- Smoother skin for three to six weeks per session.
- Thinner, lighter hair regrowth over time.
- Reduced hair density in treated areas.
- Some follicles may stop producing hair completely.
One thing to understand: Waxing isn’t a permanent solution like laser or electrolysis. Unless the follicle is destroyed, hair will return. Results depend on individual biology and commitment to regular sessions.
Key Factors That Influence Results
Not everyone gets the same results from waxing. Several factors determine how much your hair growth slows down.
Hair Type and Texture: Fine hair weakens faster than coarse hair. If you have thin, light hair, you’ll likely notice a reduction sooner. Thick, wiry hair takes longer and more consistent waxing to show results.
Hormones: Hormone levels affect hair growth. Conditions like PCOS can cause excess hair growth. In these cases, waxing alone won’t significantly reduce hair. Medical treatment may be needed alongside waxing.
Waxing Frequency: Regular waxing every four to six weeks yields better results. Skipping months allows follicles to recover. They’ll produce thicker hair again. Stick to a consistent schedule for best outcomes.
Age: Hair growth slows naturally as you age. Older adults may notice reduced regrowth faster than younger people. This isn’t just from waxing but from natural hormonal changes.
Technique and Quality: Professional waxing is more effective than DIY methods. Professionals remove hair properly from the root. Poor technique can break hair instead of pulling it out. This leads to faster, thicker regrowth.
Waxing vs. Other Hair Removal Methods
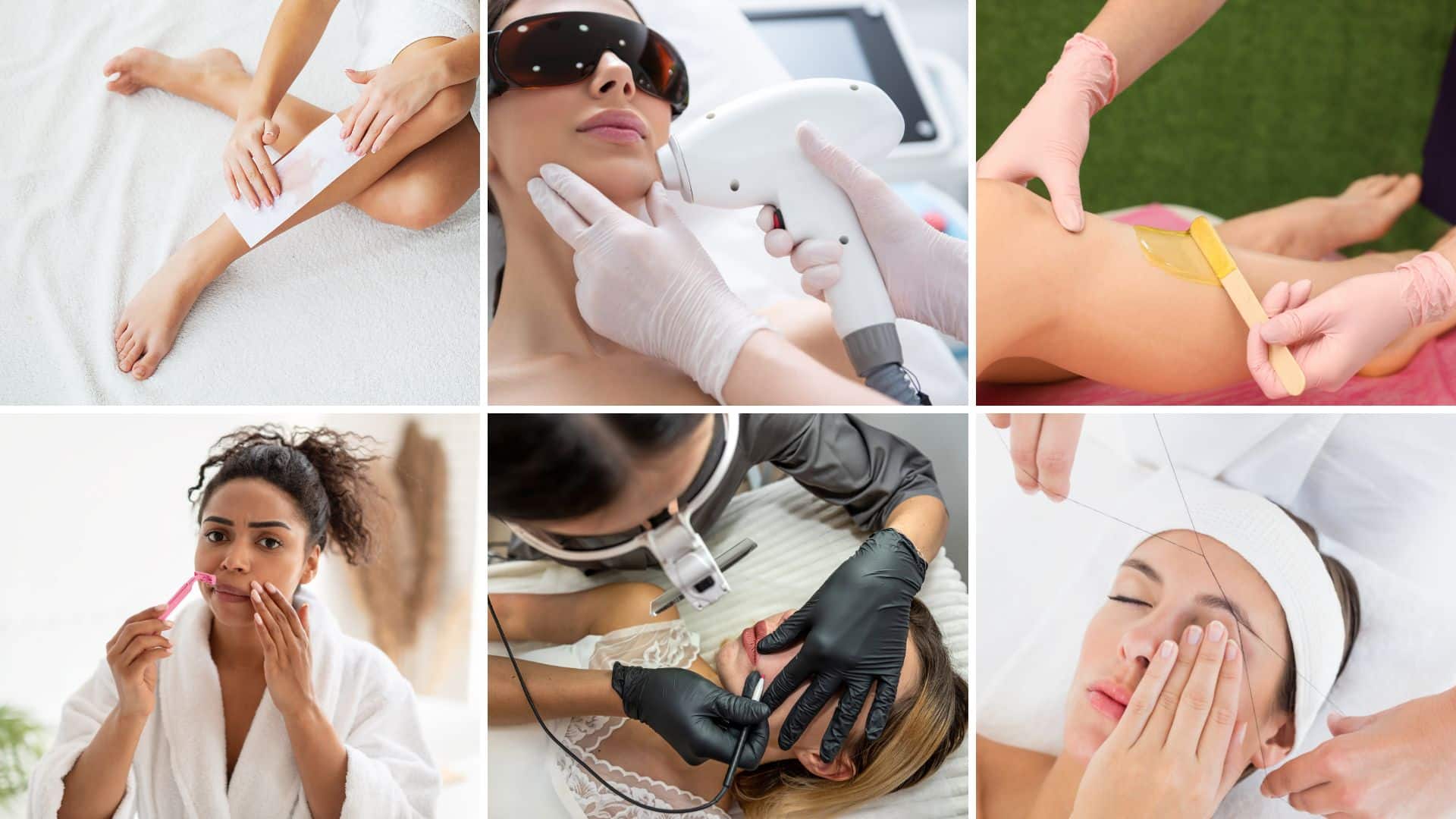

Choosing between hair removal options can be confusing. How does waxing stack up against shaving, laser, and other popular methods? Here’s a quick, straightforward comparison.
| Method | Duration | Pain Level | Reduces Growth? | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waxing | 3-6 weeks | Moderate to high | Yes, over time | Moderate |
| Shaving | 1-3 days | None | No | Low |
| Laser Hair Removal | Several months to a year | Moderate | Yes, significant reduction | High |
| Electrolysis | Permanent | High | Yes, permanent | Very high |
| Depilatory Creams | 3-7 days | None to mild | No | Low |
| Threading | 2-4 weeks | Moderate | Minimal | Low to moderate |
Important Note: For laser, smoothness lasts months once sessions are complete, but can require maintenance and may not be fully permanent for all users.
Tips to Maximize Long-Term Hair Reduction via Waxing
Want better results from your waxing routine? Following these practical tips can help you achieve smoother skin and gradual hair reduction over time.
- Wax every four to six weeks on a consistent schedule to catch hair in the growth phase and effectively weaken follicles.
- Exfoliate your skin two to three times weekly to prevent ingrown hairs and ensure smooth regrowth before your next appointment.
- Avoid shaving between waxing sessions as it disrupts the hair cycle and makes your next treatment more painful and less effective.
- Keep hair at least a quarter inch long before waxing so the wax can grip properly without causing excessive pain.
- Opt for experienced professionals who use proper waxing methods and products to remove hair completely from the root.
Common Myths & Misconceptions
Many people believe incorrect information about waxing and hair growth. Let’s clear up these common myths with facts so you can make informed decisions.
| Myth | Truth |
|---|---|
| Waxing makes hair grow back thicker | False. Hair feels coarse due to blunt tips, but the strand thickness doesn’t change at all. |
| Waxing permanently stops hair growth | Not true. Waxing reduces hair over time but isn’t permanent like electrolysis. |
| Waxing is the same as plucking | Incorrect. Waxing removes multiple hairs from large areas at once. Plucking targets individual hairs only. |
| You should wax every two weeks | It’s a bad idea because it will irritate the skin and doesn’t give hair enough time to grow properly between sessions. |
| Hair grows back darker after waxing | False. You’re seeing new growth, which appears darker. Waxing doesn’t change your natural hair pigment. |
| Waxing is only for women | Anyone can wax. Men regularly wax backs, chests, and other areas. It’s a personal grooming choice. |
Wrapping It Up
To summarize, so, does waxing reduce hair growth? Yes, it can, but results vary from person to person.
With steady waxing over time, hair roots may weaken, leading to slower, softer regrowth overall. However, waxing isn’t a permanent solution like electrolysis.
It’s a temporary method that offers gradual reduction with consistency. Your hair type, hormones, and waxing frequency all play a role in results.
If you want smoother skin and less hair over time, stick to a regular waxing schedule. Give it at least six months before judging results.
Have you noticed changes in your hair growth from waxing? Share your experience in the comments below.